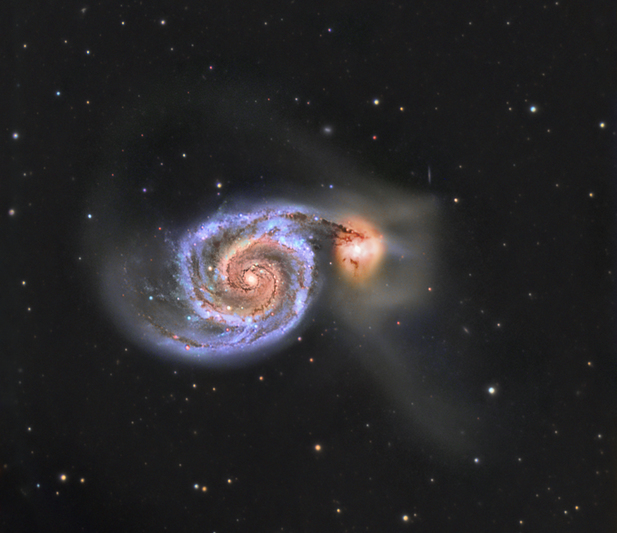
M51 - The Whirlpool galaxy
|
The Whirlpool Galaxy, also known as M51 or NGC5194, is an interacting grand-design spiral galaxy with a Seyfert 2 active galactic nucleus in the constellation Canes Venatici. It was the first galaxy to be classified as a spiral galaxy. Recently it was estimated to be 23 ± 4 million light-years from the Milky Way, but different methods yield distances between 15 and 35 million light-years. Messier 51 is one of the best known galaxies in the sky. The galaxy and its companion, NGC5195, are easily observed by amateur astronomers, and the two galaxies may even be seen with binoculars.
What later became known as the Whirlpool Galaxy was discovered on October 13, 1773 by Charles Messier while hunting for objects that could confuse comet hunters, and was designated in Messier's catalogue as M51. Its companion galaxy, NGC 5195, was discovered in 1781 by Pierre Méchain, although it was not known whether it was interacting or merely another galaxy passing at a distance. It was, however, not until 1845 that William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, found the Whirlpool possessed a spiral structure, the first known "nebula" to be known to have one. Details M: Avalon LInear Fast Reverse T: Celestron C9.25 with 0.63x reducer C: Atik 460EXM with Baader LRGB filters 50x600s 2xbin Luminance 50x180s Red, Blue and Green - A total integration time of 15.5 hours |